Welcome to the website of Hebi Yuxing Coal Machinery Co., Ltd.!
Hotline:
Installation and Adjustment of Multi-Rope Friction Guide Wheel Device
2022-07-07
Multi-rope friction guide wheel device:
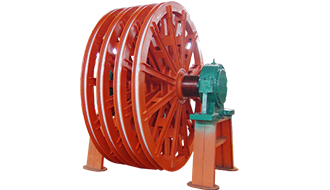
(1) The function of the guide wheel
Guide wheels are used in tower-type multi-rope friction hoists, with one set installed on each hoist unit at the lower level of the machine room. Their primary function is to adjust the spacing between the hoisting containers according to the requirements of the lifting system, while also increasing the wrap angle of the wire ropes around the friction wheel.
When the diameter of the friction wheel exceeds the distance between the two hoisting containers—or between a container and its counterweight—it becomes necessary to install guide wheels in order to bring the wire ropes closer together on either side of the friction wheel, ensuring the required center-to-center distance between the two containers. Alternatively, if a wrap angle greater than 180° is needed (typically ranging from 180° to 195°), guide wheels must also be fitted.
(2) Specifications of the guide wheel
① The nominal diameter is the same as the nominal diameter of the friction wheel.
② The number of wheel bodies is equal to the number of ropes on the hoist.
③ The rope pitch and groove diameter are the same as those of the friction wheel.
(3) Structural Overview
The guide wheel has a structure essentially identical to that of the sheave assembly, primarily consisting of components such as the shaft, fixed wheel, floating wheel, bearing bushings, rolling bearings, shims, bearing housings, and bearing beams. One of the wheels (the fixed wheel) is connected to the shaft via a flat key. As the wire rope moves, it drives the fixed wheel to rotate, which in turn causes the shaft of the guide wheel to spin along with it. The remaining wheels, however, are designed to slide freely on the guide wheel’s shaft; their hubs are press-fitted with wear-resistant copper sleeves, whose inner diameters form a clearance fit with the shaft, allowing the wheels to rotate relatively freely around it. These are referred to as "floating wheels."
Both the fixed wheel and the floating wheel feature an integral design, constructed by welding together the wheel hub, wheel rim, and several channel-shaped steel sections acting as spokes. Between the floating wheel’s hub and the shaft, four semi-bushings—typically made of copper—are installed to ensure smooth operation. To maintain flexibility in wheel movement, a slight axial clearance of 0.2 to 0.5 mm is maintained between each wheel, preventing interference during relative rotation.
When the linear speeds of the individual wire ropes differ slightly, the floating wheel can freely rotate relative to the shaft. Additionally, the wheel rim is fitted with specially designed liners—currently often made from nylon—to minimize friction between the wire rope and the rim, thereby significantly extending the lifespan of the wire rope. Finally, both ends of the shaft are supported by spherical thrust roller bearings.
(4) Installation and Adjustment
During installation, the distance from the centerline of the guide wheel to the right-side bearing housing foundation must meet the drawing requirements and should not be less than the value indicated on the drawing.
During installation, both ends of the bearing should be cleaned thoroughly, then filled with grease—specifically lithium-based grease grade 2# or 3#. The amount of grease applied should completely fill the bearing and occupy approximately 1/3 to 1/2 of the space within the bearing housing. Ensure the bearing rotates smoothly afterward.
During installation, the right-end bearing cap should directly press against the outer race of the bearing, while a gap of at least 1.5 mm must be maintained between the left-end bearing cap and the outer race.
During installation, the bearing shells should be removed and cleaned. After cleaning, when reassembling, make sure to apply a generous layer of grease into the oil grooves on both halves of the shell as well as onto the shells themselves.
Follow us

Hebi Yuxing Coal Machinery Co., Ltd.
Hotline:+86-13939219076
Technical Consultation:+86-13503925535
Address: Yuxing Industrial Park, Shancheng, Hebi City, Henan Province
You are a helpful assistant.
Copyright © Hebi Yuxing Coal Machinery Co., Ltd. SEO tags Business license
Copyright © Hebi Yuxing Coal Machinery Co., Ltd.Business license
This website supports IPv6 and SEO tags.